 PDF(10887 KB)
PDF(10887 KB)


Intelligent hazard detection method for super high arch dam construction based on enhanced semisupervised contrastive learning
Mingchao LI, Yuangeng LÜ, Qiubing REN, Leping LIU, Zhiyong QI, Dan TIAN
Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology) ›› 2025, Vol. 65 ›› Issue (10) : 1838-1852.
 PDF(10887 KB)
PDF(10887 KB)
 PDF(10887 KB)
PDF(10887 KB)
Intelligent hazard detection method for super high arch dam construction based on enhanced semisupervised contrastive learning
Objective: Timely hazard detection during the construction of super high arch dams is crucial for reducing engineering accidents and ensuring project safety. Hazards in such settings are often hidden and diverse, making them difficult to detect during early-stage conventional inspections. However, fragmented hazard records at construction sites are crucial for identifying and detecting issues early, helping management personnel to promptly assess potential engineering risks. Methods: This study proposes an intelligent hazard identification method for super high arch dam construction using enhanced semisupervised contrastive learning. A multisource classification model for hazard text is developed to categorize and assess hazard types and levels from fragmented hazard texts, establishing a systematic hazard inspection framework. The model is built on the Transformer architecture, effectively capturing the semantic and positional relationships inherent in hazard descriptions. A contrastive learning module improves the Transformer by leveraging interclass relationships to amplify the differences between dissimilar samples. This significantly enhances classification accuracy, especially for multi-source attribute hazard categories. The method integrates self-supervised and supervised learning, emphasizing interclass distinctions while making use of label content. A memory bank mechanism decouples training batches, enabling comprehensive collection of negative samples, thereby enhancing the performance of semisupervised contrastive learning. Finally, the hazard category and level identification results are combined to visualize safety hazard distributions. Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) is used to extract latent clues for hazard risk inspection, constructing structured hazard inspection tables for different levels of risk. These tables allow managers to prioritize inspections in high-risk areas, enhancing the efficiency and precision of hazard detection. Results: The results show that the proposed classification model significantly improves hazard type and hazard level recognition tasks, with F1 score improvements of 4.9% and 3.3%, respectively. Multidimensional experiments were conducted to validate its significant advantages: 1) Analyzing the influence of different Memory Bank sizes on model performance highlighted the importance of batch decoupling batches and the selection of a robust number of negative samples; 2) Ablation experiments validated the contribution of each module to the model's performance improvement; 3) Dimensionality reduction clustering using t-SNE visually confirmed the contrastive learning module's ability to effectively group similar classification samples; 4) A comparison of infoNCE loss between this model and the base Transformer demonstrated the practical benefits of the contrastive learning module during training; 5) Performance comparisons with common classification models showed the proposed model's significant advantages in overall accuracy. The hazard category and level identification results are used to extract key topic information using the LDA topic model, revealing the potential risks present in the current hazard categories and levels. Taking "High-altitude fall" as an example, key topic clustering was applied to compile a complete hazard inspection clue table structured by hazard levels. Conclusions: The method enhances the precision and systematization of hazard identification during the construction of super high arch dams. It introduces a refined multi-source attribute hazard identification method, providing a novel approach to intelligent safety management in engineering and promoting the development of hazard management toward automation and intelligence.
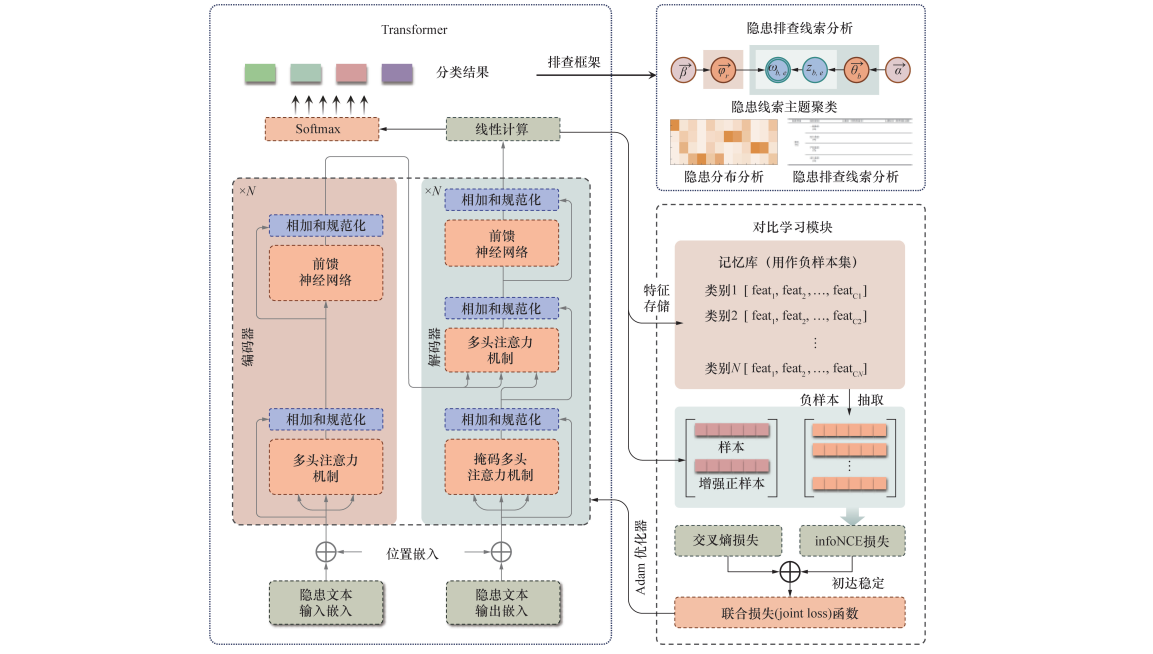
super high arch dam / construction hazard detection / text classification / enhanced semisupervised contrastive learning / memory bank / topic model
| 1 |
顾冲时, 苏怀智, 刘何稚. 大坝服役风险分析与管理研究述评[J]. 水利学报, 2018, 49 (1): 26- 35.
|
| 2 |
姚可夫, 田始光, 漆一宁, 等. 高海拔区特征环境驱动下混凝土坝服役性能研究进展[J]. 水利学报, 2023, 54 (6): 717- 728.
|
| 3 |
王飞, 刘金飞, 尹习双, 等. 高拱坝智能进度仿真理论与关键技术[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 61 (7): 756- 767.
|
| 4 |
谭尧升, 樊启祥, 汪志林, 等. 白鹤滩特高拱坝智能建造技术与应用实践[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 61 (7): 694- 704.
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
王晓玲, 王栋, 任炳昱, 等. 高拱坝混凝土振捣机器人系统研发及应用[J]. 水利学报, 2022, 53 (6): 631-643, 654.
|
| 7 |
樊启祥, 周绍武, 林鹏, 等. 大型水利水电工程施工智能控制成套技术及应用[J]. 水利学报, 2016, 47 (7): 916-923, 933.
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
刘婷, 张社荣, 王超, 等. 水利施工事故文本智能分析的BERT-BiLSTM混合模型[J]. 水力发电学报, 2022, 41 (7): 1- 12.
|
| 12 |
李明超, 田丹, 沈扬, 等. 融入Attention机制改进Word2vec技术的水利水电工程专业词智能提取与分析方法[J]. 水利学报, 2020, 51 (7): 816- 826.
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
钟登华, 时梦楠, 崔博, 等. 大坝智能建设研究进展[J]. 水利学报, 2019, 50 (1): 38-52, 61.
|
| 15 |
杨阳蕊, 朱亚萍, 陈思思, 等. 融合群体智能策略的AI链在大坝防汛抢险知识推理中的应用[J]. 水利学报, 2023, 54 (9): 1122- 1132.
|
| 16 |
李庆斌, 马睿, 胡昱, 等. 大坝智能建造研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 62 (8): 1252- 1269.
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
王仁超, 张毅伟, 毛三军. 水电工程施工安全隐患文本智能分类与知识挖掘[J]. 水力发电学报, 2022, 41 (11): 96- 106.
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
张晓健, 张栋梁, 李明超, 等. 面向质量检测的混凝土坝施工规范智能检索[J]. 水力发电学报, 2023, 42 (4): 114- 125.
|
| 26 |
廖才波, 黄智勇, 杨金鑫, 等. 基于缺陷文本识别的变压器风险评估及辅助检修决策方法[J]. 高电压技术, 2024, 50 (7): 2931- 2941.
|
| 27 |
武红鑫, 韩萌, 陈志强, 等. 监督和半监督学习下的多标签分类综述[J]. 计算机科学, 2022, 49 (8): 12- 25.
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
邢宇杰, 王啸, 石川, 等. 基于节点特征对抗性攻击的图对比学习鲁棒性验证[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 64 (1): 13- 24.
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
BULAT A, SÁNCHEZ-LOZANO E, TZIMIROPOULOS G. Improving memory banks for unsupervised learning with large mini-batch, consistency and hard negative mining[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Toronto, ON, Canada: IEEE, 2021: 1695-1699.
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
李明超, 吕沅庚, 田丹, 等. 基于改进LDA的水电工程进度管理文本智能分析[J]. 水力发电学报, 2022, 41 (3): 133- 141.
|
| 39 |
VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[J/OL]. (2017-06-12)[2024-12-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762.
|
| 40 |
李凯, 任炳昱, 王佳俊, 等. 基于CEEMDAN-Transformer的灌浆流量混合预测模型[J]. 水利学报, 2023, 54 (7): 806- 817.
|
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
|
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
中华人民共和国水利部. 水利水电工程施工安全管理导则: SL 721—2015[S]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2015.
Ministry of Water Resources of the People's Republic of China. Guidelines for construction safety management of water and hydropower projects: SL 721-2015[S]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
|
| 45 |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |